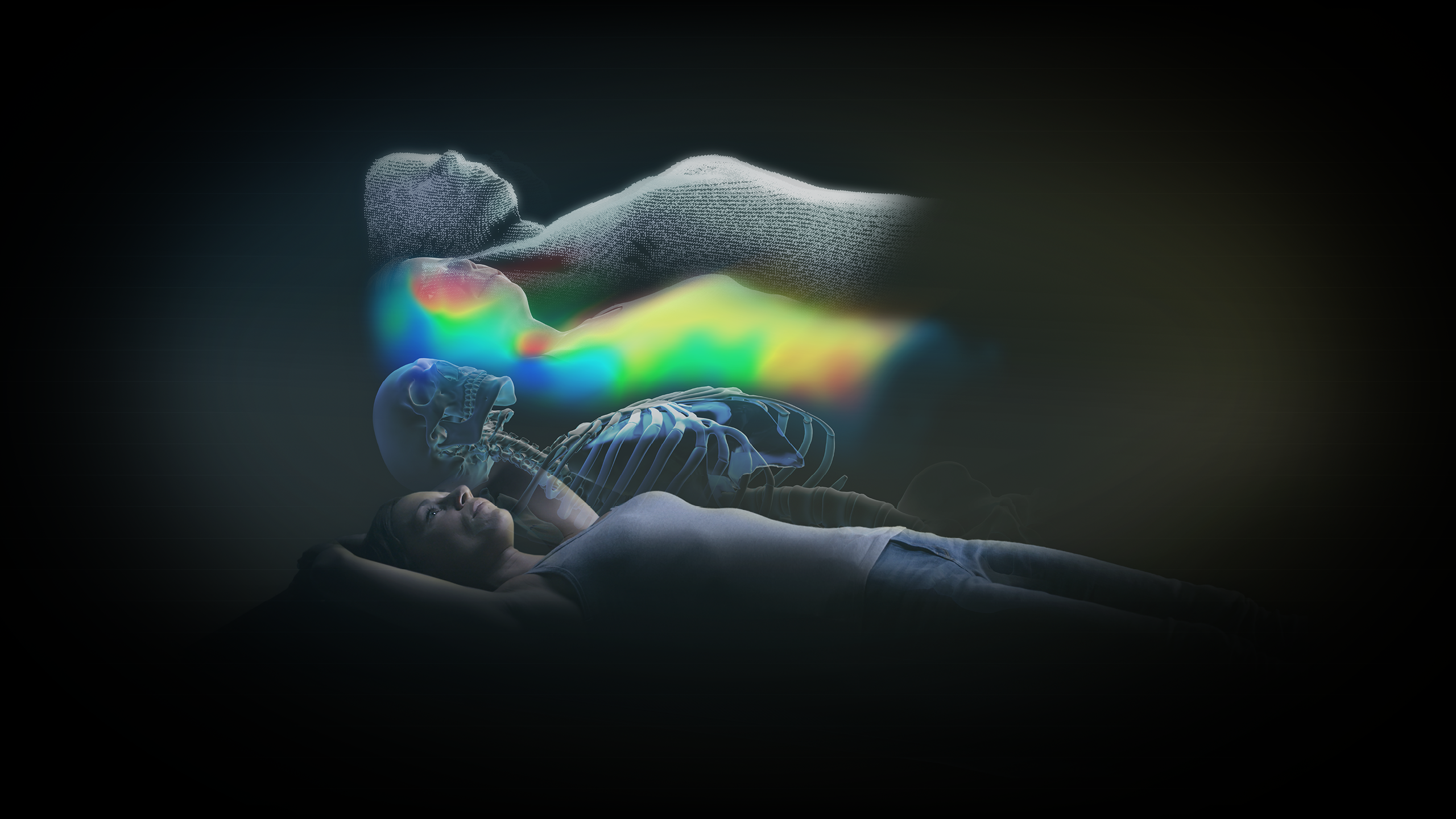
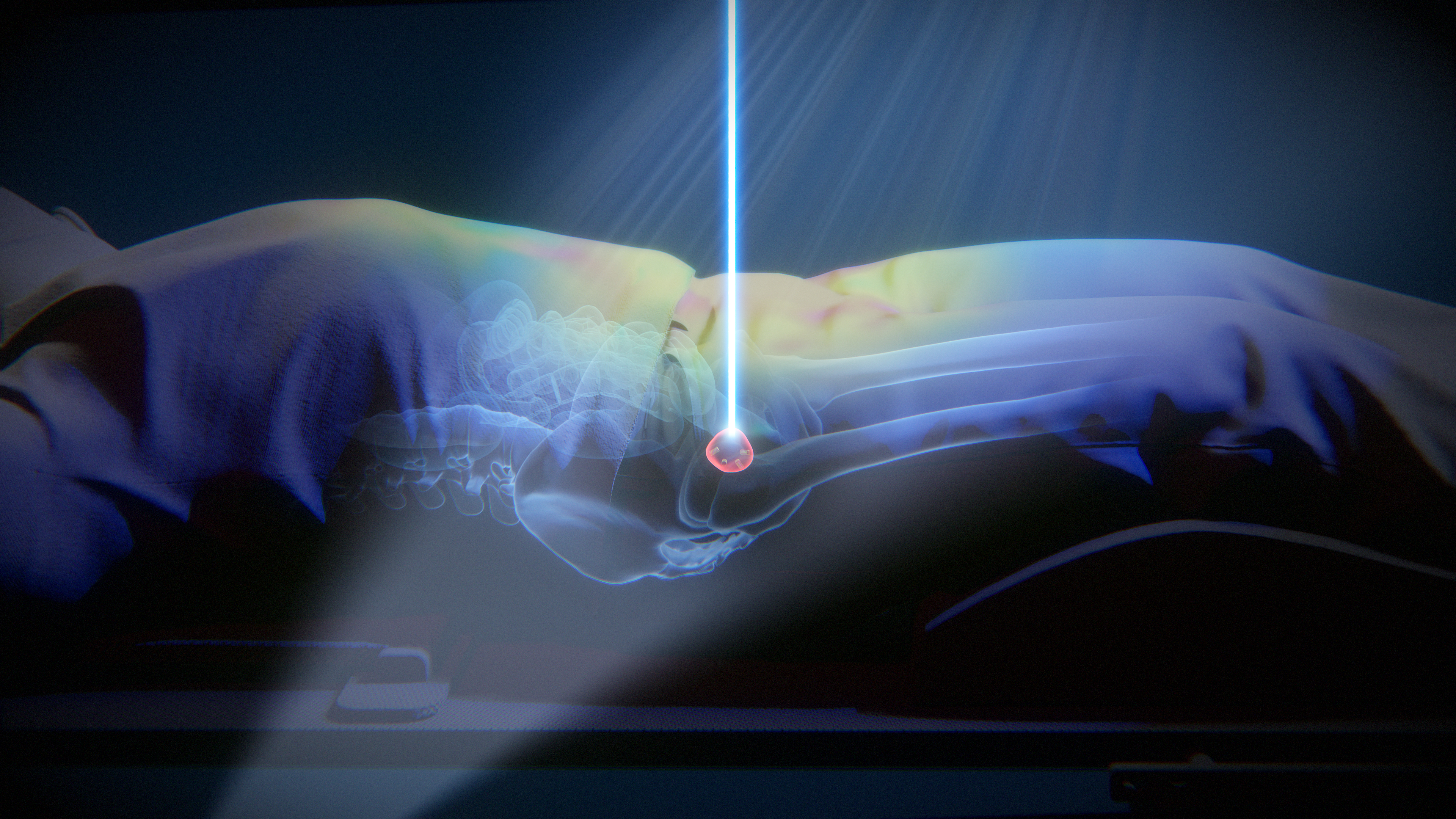
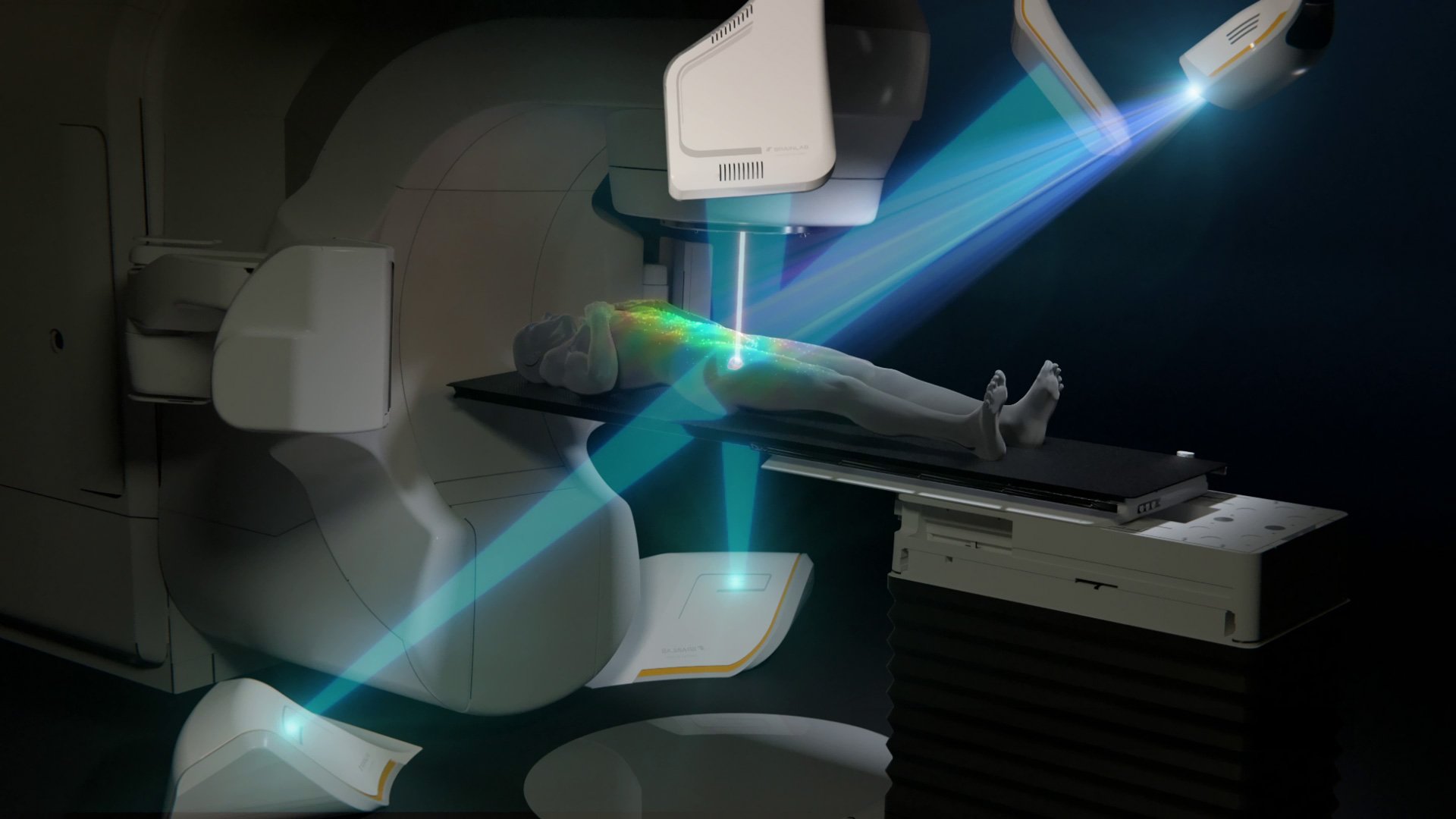
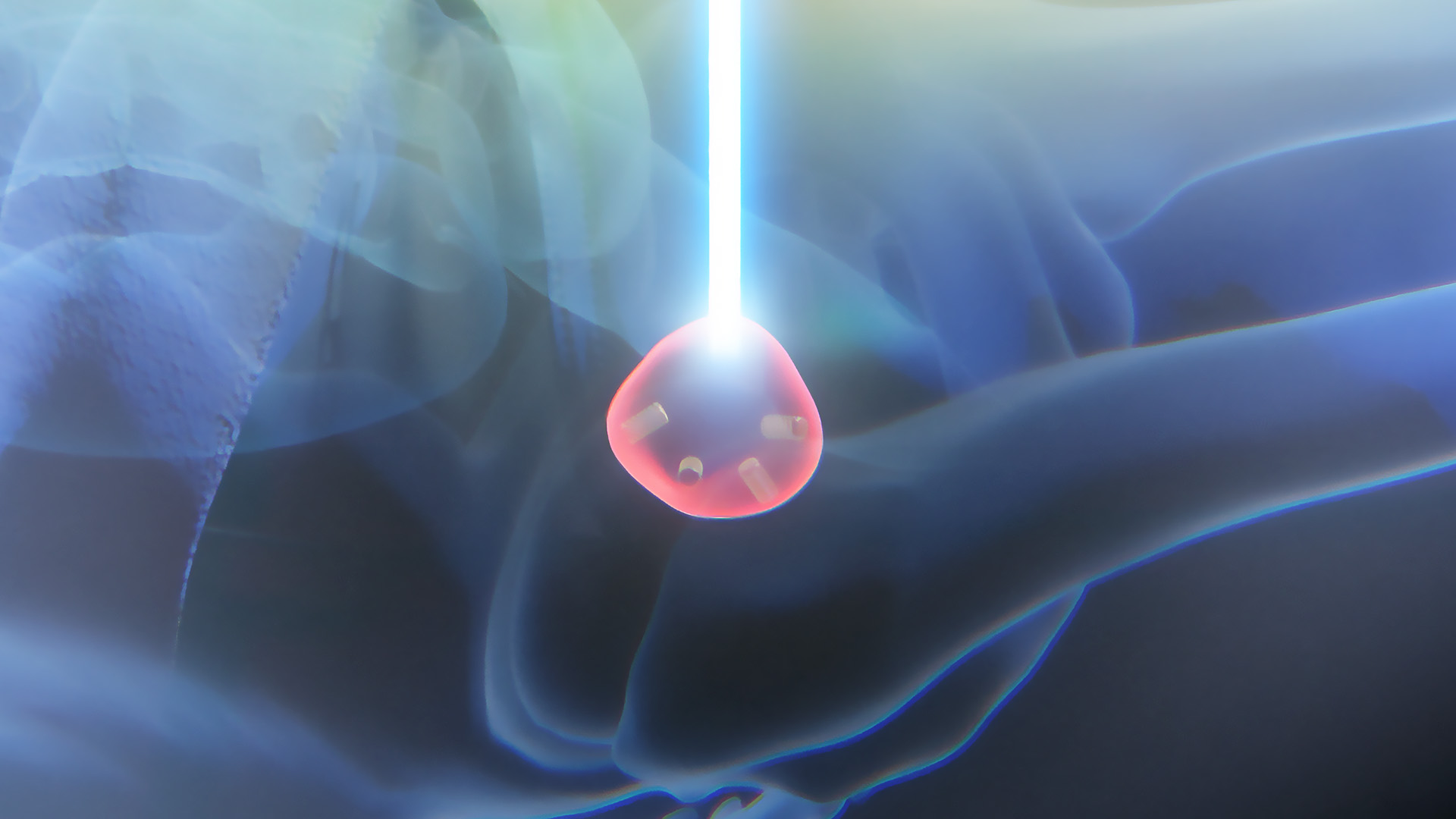
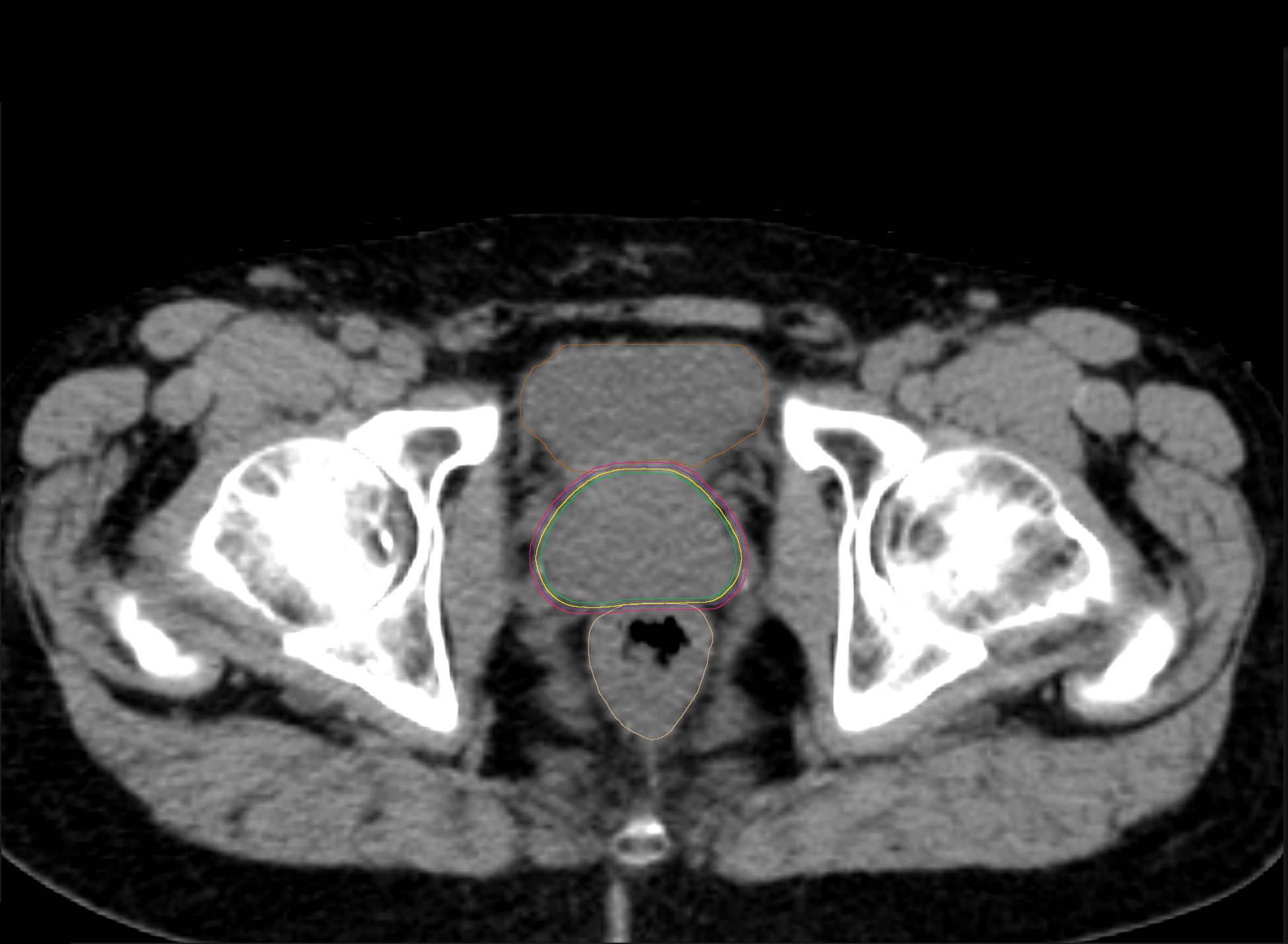
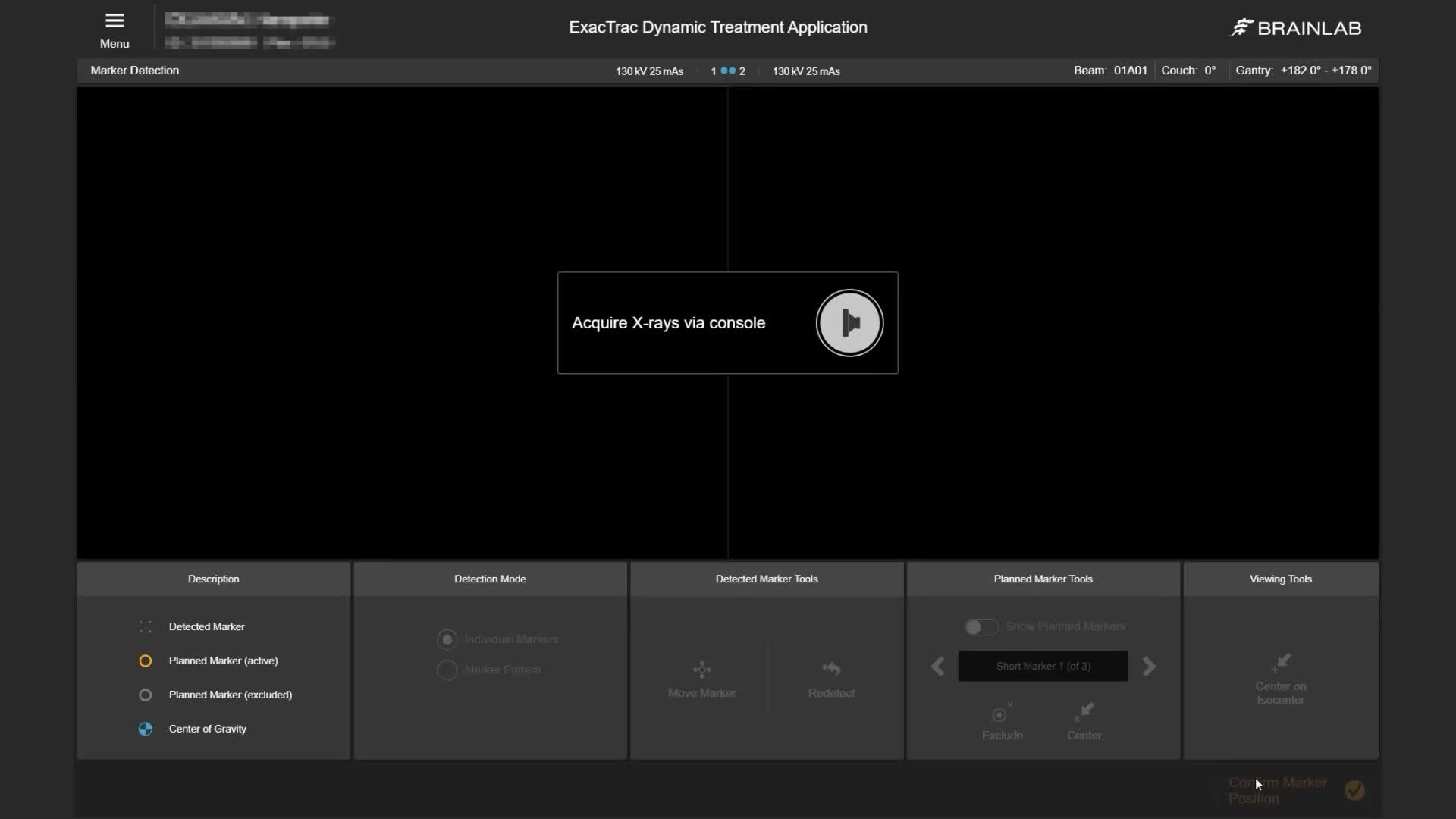
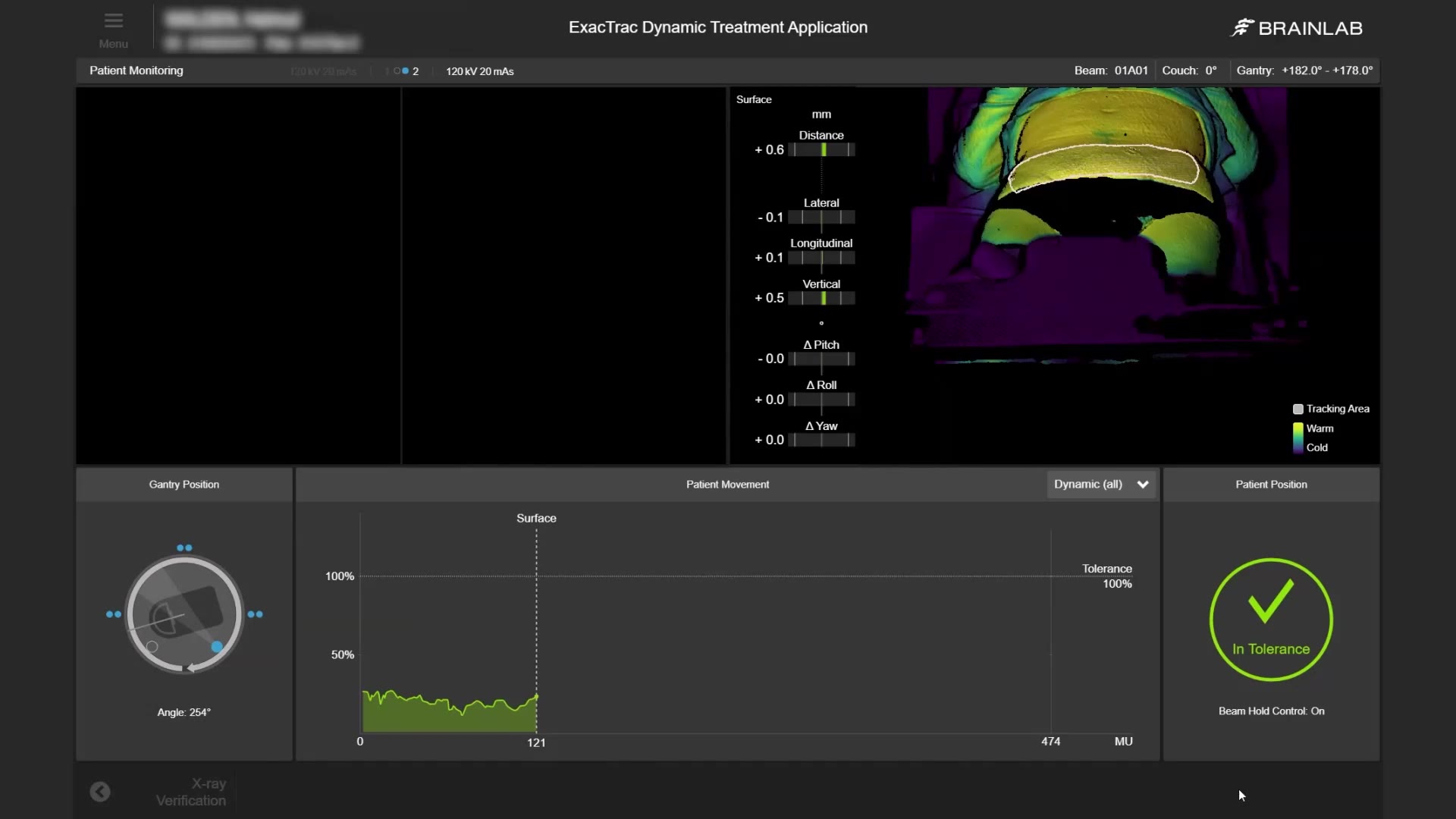
ExacTrac Dynamic Implanted Marker Workflow enables precise positioning and monitoring of highly mobile soft tissue tumors, like prostate cancer, when using fiducials to represent the position of the target volume. It can identify and correct intrafractional movements, such as prostatic drifts, mid-treatment to deliver high doses with sub-millimetric accuracy.
Hear from experts in the field
Power and precision in prostate care
Prostate cancer is the second most commonly diagnosed cancer in men, with an estimated 1.4 million diagnoses and almost 400,000 deaths worldwide in 20221. Prostate tumors grow in highly mobile soft tissue, posing a challenge for treatment compared to static tumors. ExacTrac Dynamic Implanted Marker Workflow helps you address these challenges with precise target volume positioning and low-dose monitoring for highly accurate radiation. Transform your external body radiation therapy (EBRT) practice into SBRT for prostate cancer using fiducial markers to ensure precise treatment delivery.

Quantifying clinical success
Precision in prostate care starts here
See how the Implanted Marker Workflow can optimize prostate cancer treatments.
See ExacTrac Dynamic in action
Interested in better understanding the capabilities of the Implanted Marker Workflow for prostate cancer treatment?
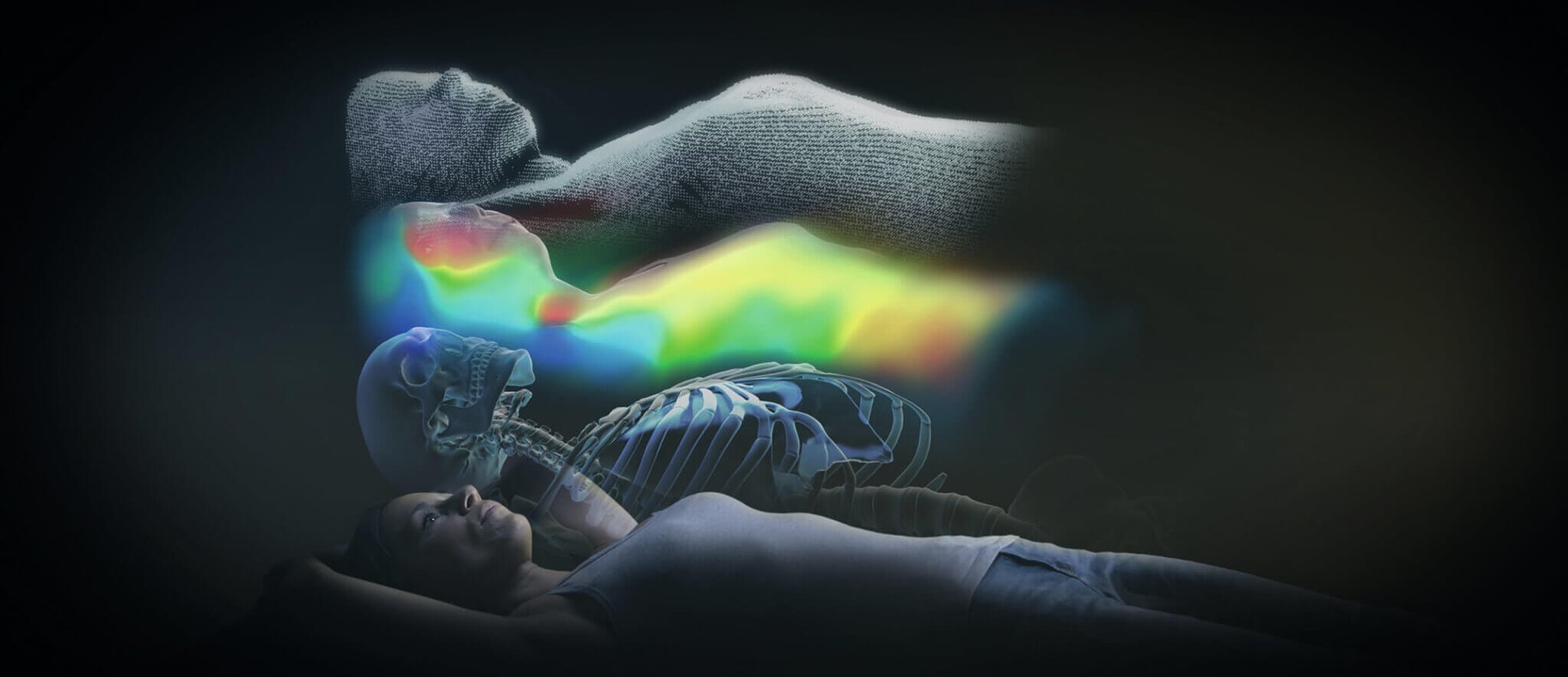
ExacTrac Dynamic
Achieve precise tumor treatment with ExacTrac Dynamic thermal-surface camera and low-dose x-ray tracking for accurate positioning and monitoring.
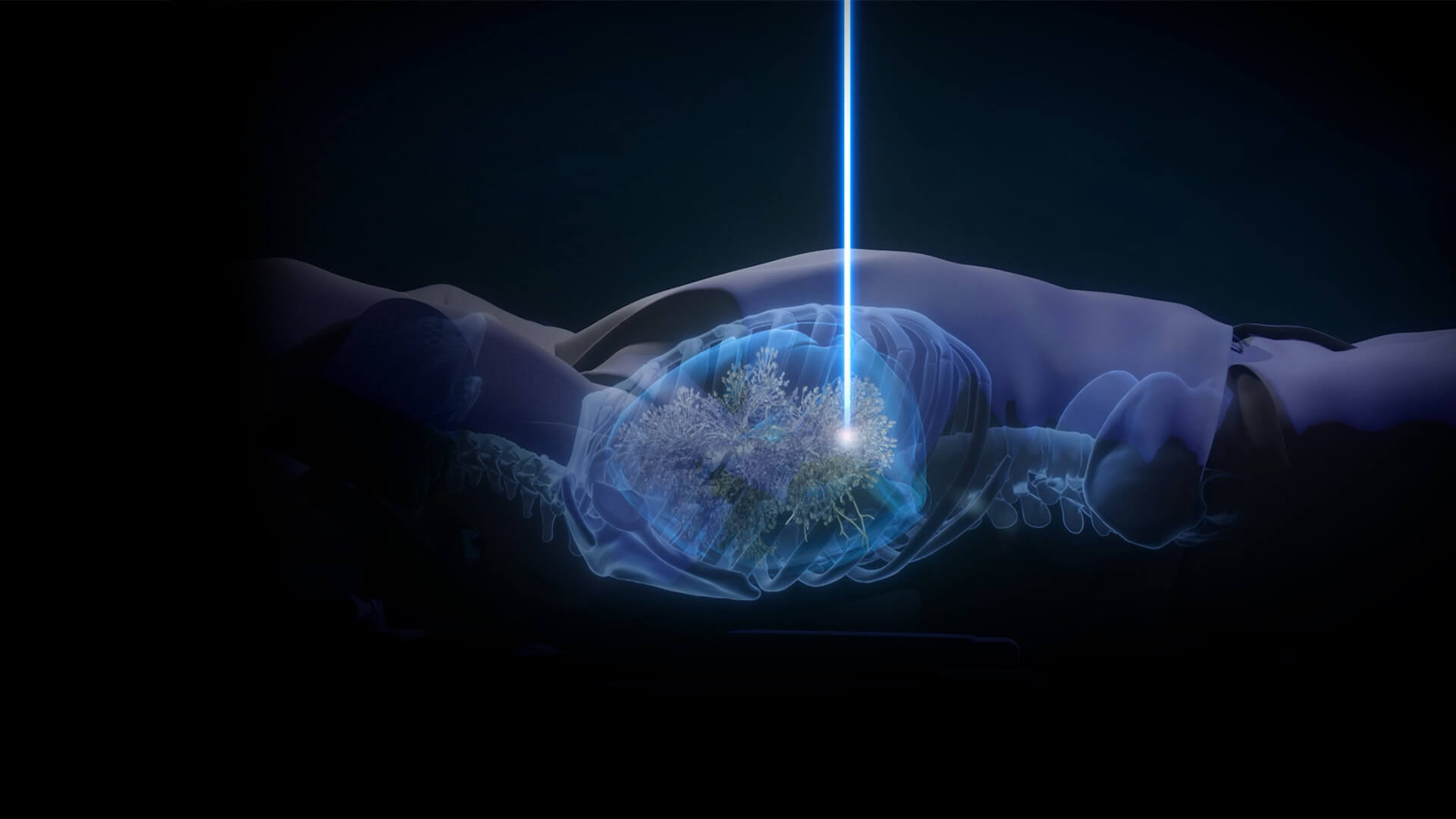

Lung Motion Management
Enhance lung cancer treatment accuracy with ExacTrac Dynamic integrated Lung Motion Management3, tracking tumor motion due to breathing.

Brainlab Novalis Knowledge
The objective of the Brainlab Novalis Knowledge Program is to keep our customers up to date with the latest research in the field of radiosurgery. The program consists of four uniquely tailored services that train, connect, advance and certify all involved specialties.
Experience precision in prostate cancer treatment
Culp, M.B., et al. Recent Global Patterns in Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates. Eur Urol, 2020. 77: 38. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31493960.
Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Laversanne M, Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I, Bray F (2024). Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available from: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today, accessed [13 November 2024]. https://gco.iarc.who.int/media/globocan/factsheets/cancers/27-prostate-fact-sheet.pdf.Kishan et al., JAMA Oncol. 2023 Mar 1;9(3):365-373. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.6558 | Reduction from 43.4% to 24.4% for grade ≥2 genitourinary (GU) toxicity and reduction from 10.5 % to 0.0% for grade ≥2 gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity.
Not yet commercially available.