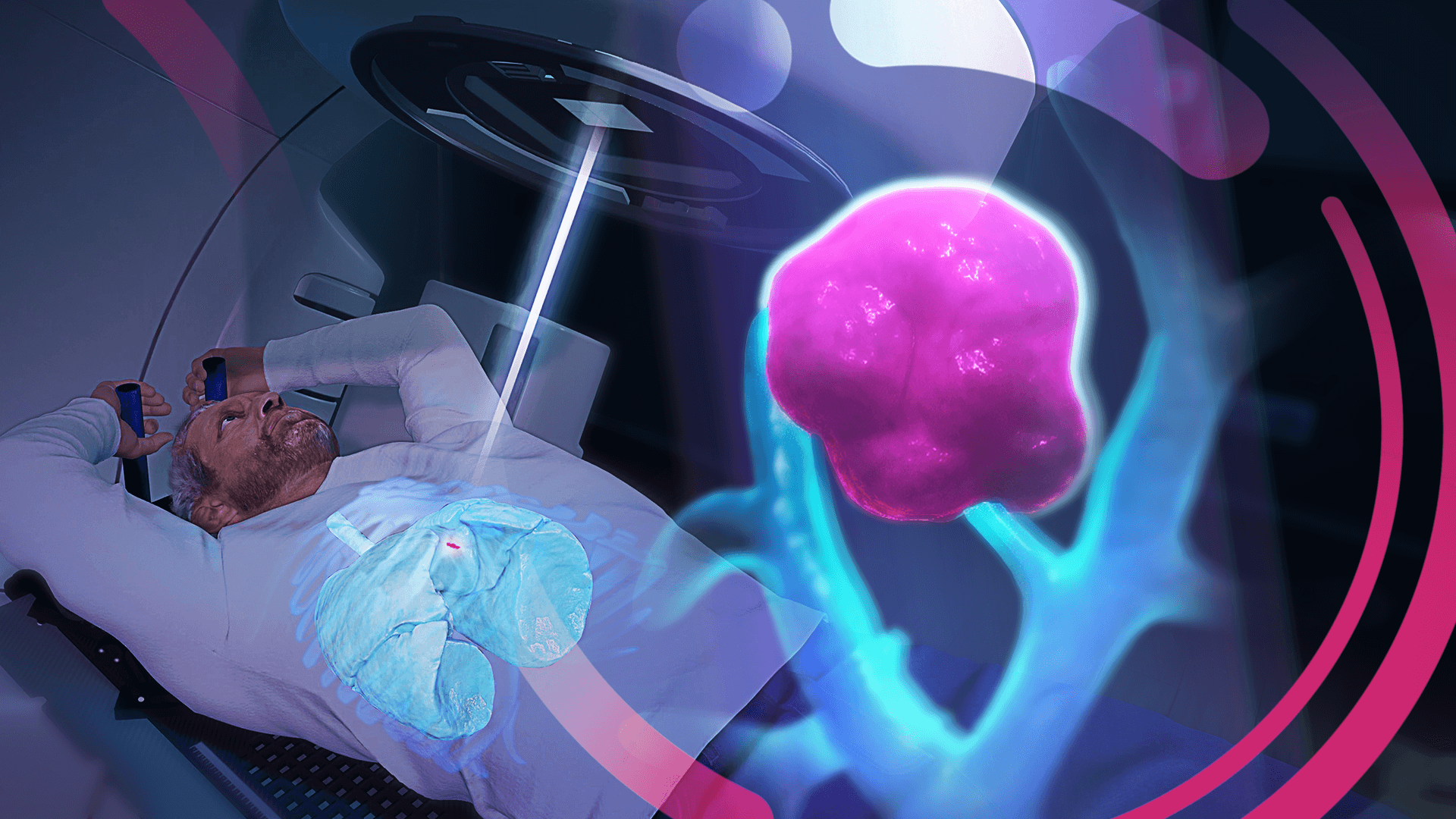
Lung Motion Management1 aims to enable the imaging of even the smallest of lung tumors in motion for high-precision, non-invasive radiotherapy.
Not all technical capabilities and clinical applications depicted in this section for the purpose of illustrating the product vision are available in the current product release. However, most capabilities are in clinical use in previous product generations. With specific questions reach out to Brainlab.
According to the American Cancer Society
Early-stage Lung Cancer Diagnosis –
Treatment with Innovative Technology
Virtual Treatment:
Interactive Session for Understanding Lung Irradiation
FAQ
What are the main benefits of using ExacTrac Dynamic®?
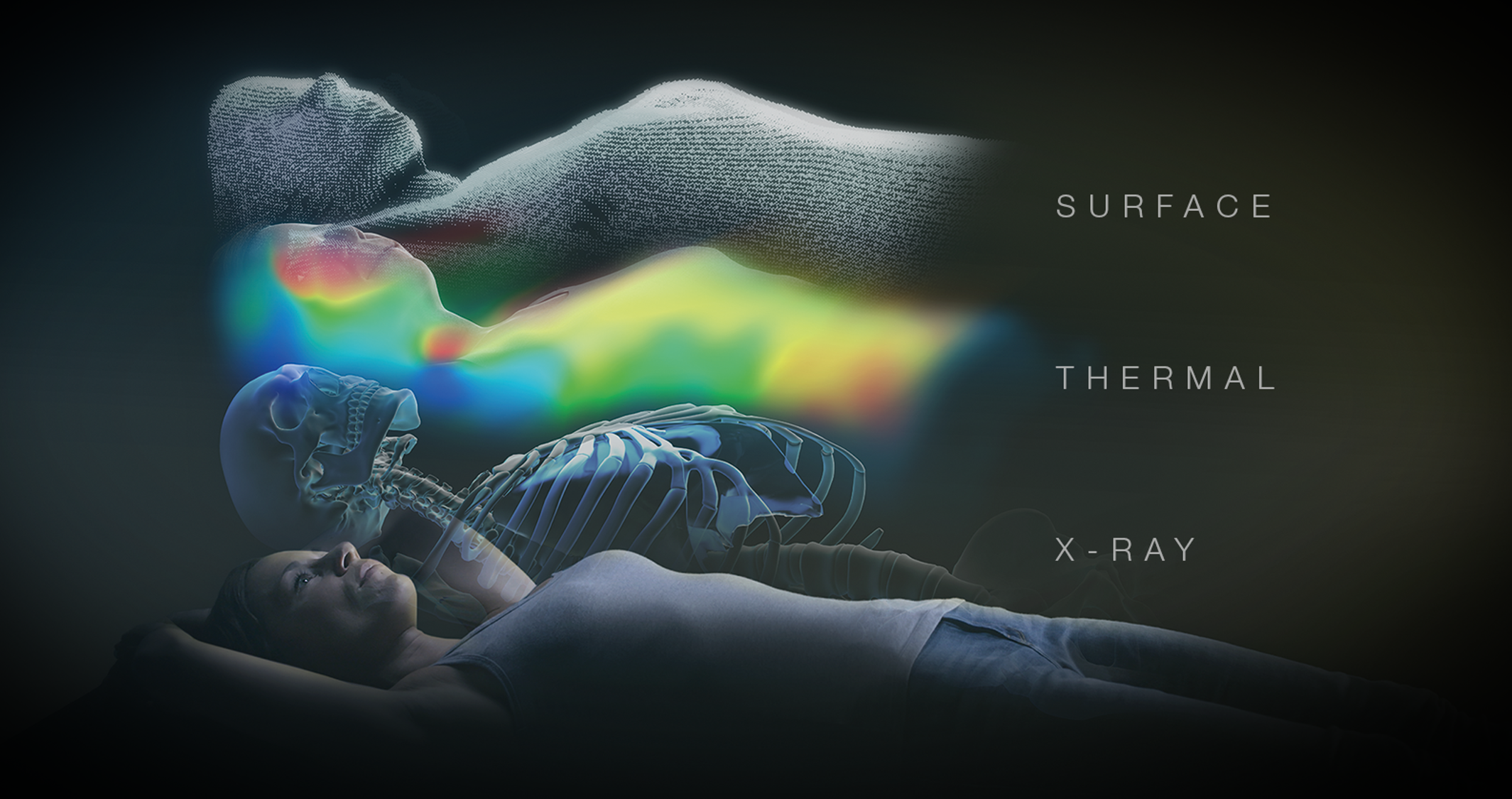
ExacTrac Dynamic® delivers high-precision radiotherapy by using a thermal surface camera to continuously track the patient’s position during treatment and by verifying the position of the tumor with x-ray imaging. The ExacTrac Dynamic® system is seamlessly integrated with standard linear accelerators and thereby facilitates efficient and precise treatment sessions for a wide range of indications.
What does 4D-CT mean, and how is this technology currently being used?
4D-CT, or four-dimensional computed tomography, is an advanced imaging method that captures the location and movement of a patient’s tumor and organs over time. 4D-CT is currently used in the field of radiotherapy, especially for liver and lung indications.
To create 4D-CT scans, several standard CT scans are acquired while the patient is breathing freely. The images are then sorted according to the respiratory status. In this way, several “bins” are obtained, each representing a specific respiratory status at a certain time point, which adds the fourth dimension to an otherwise three-dimensional CT-scan.
Ultimately, 4D-CT scans provide a precise analysis of the tumor movement which enables more accurate radiotherapy planning. In this way, radiation is administered either on the entire area in which the tumor moves, the “motion envelope,” or during specific moments of the respiration cycle (currently under development at Brainlab).
What does tracking surrogate mean?
The word surrogate means replacement and, in this case, refers to the surrounding tissue of a small lung tumor that moves along with it during respiration. Since very small tumors often cannot be adequately depicted and captured with imaging tools, a tracking surrogate is used to track the movement of the tumor.
How much lower is the 2D x-ray dose from ExacTrac Dynamic® compared to the cone-beam CT?
The dose of a 2D x-ray or conventional x-ray is about fifty times smaller than the dose of a cone-beam CT. (De Los Santos et al., Int J Radiation Oncol Biol Phys, 2013; Cheng et al., Radiat. Prot. Dosim, Vol 175, Iss 3, 2017)
Which indications can be treated with ExacTrac Dynamic®?
The previous product version, ExacTrac®, enabled us to gather many years of experience and expertise in the irradiation of cranial, spine, prostate and liver tumors. In addition, ExacTrac Dynamic® is also in use for the treatment of breast cancer and, in the future, will be available to use for the treatment of lung cancer. Currently more than 1.000 ExacTrac® and ExacTrac Dynamic® systems are being used clinically worldwide.
Is the Lung Motion Management* method already in use?
The Lung Motion Management method is partially in use through the combination of ExacTrac® and Vero®. However, these products are being used without the support of motion analysis for the localization of very small tumors and without thermal surface camera tracking for continuous monitoring of the patient’s position (infrared markers only). Nevertheless, the Vero® system already works with a correlation model built from temporal information of external respiratory motion (infrared markers) and localized internal target position (x-ray fluoroscopy). During treatment, the correlation model is used to predict the target position, which can continuously be verified by x-ray imaging. The information obtained from the verification images can be used to update the correlation model.
* Commercially not available.
How does this method compare to Deep Inspiration Breath Hold (DIBH)?
Our system will also support DIBH for pulmonary indications, but the choice of treatment approach is and remains up to the treating medical staff. However, based on clinical experience, we know that patients suffering from lung cancer do not breathe in as deeply or cannot hold their breath for a sufficiently long time. With the Lung Motion Management* method, the lung tumor is also irradiated during exhalation, i.e., in the more stable phase of the respiratory cycle.
*Commercially not available.