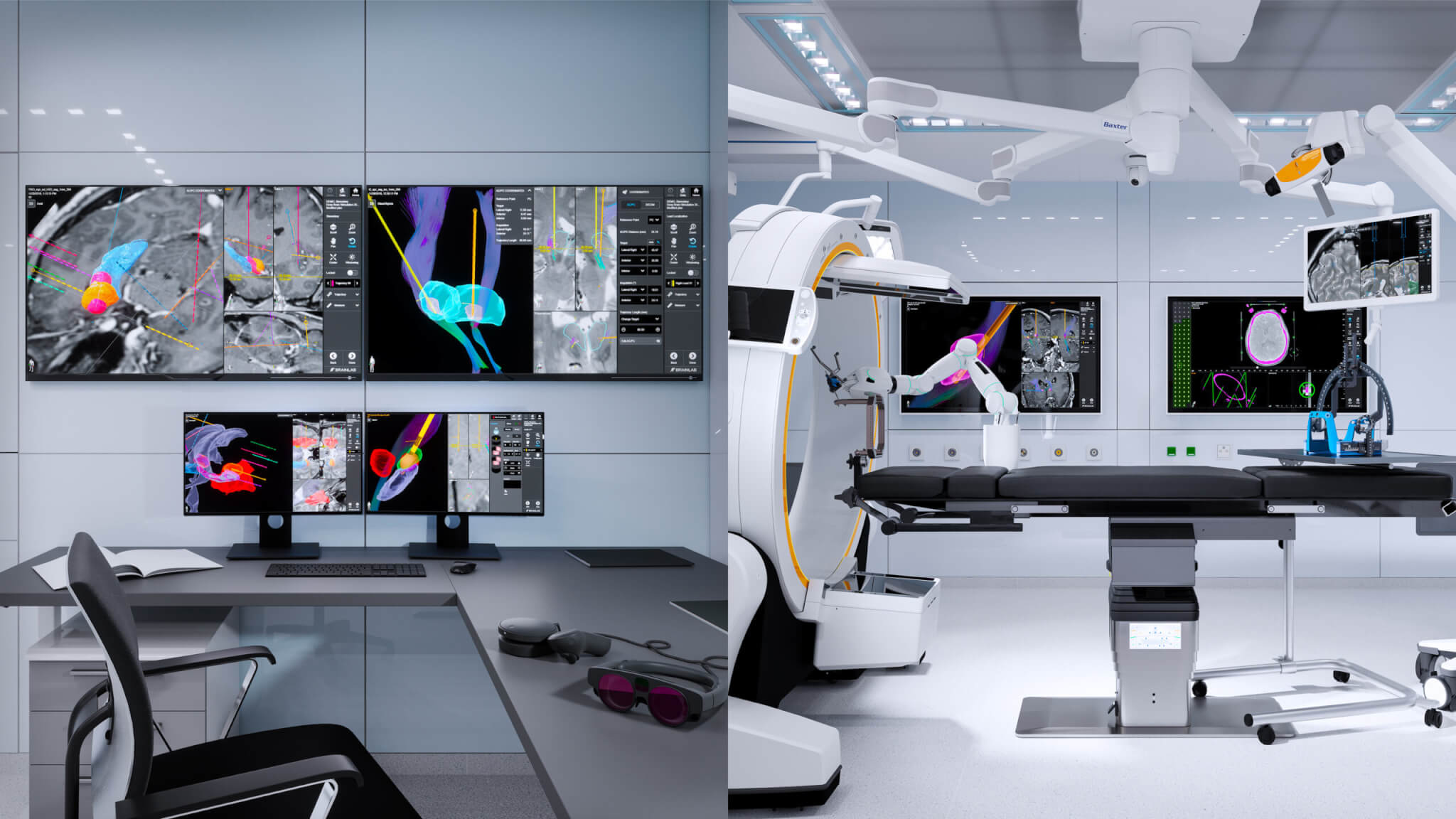
As we look toward the future, our mission is to address the unmet needs of patients suffering from neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, dystonia, essential tremor and drug-resistant epilepsy.
Origins
In the past, the ability to identify brain targets on patient imaging was highly limited due to a lack of contrast and clear image resolution.
As such, procedures like deep brain stimulation (DBS) historically relied on additional workflow steps such as intraoperative electrophysiology and clinical tests that needed to be conducted while the patient was awake.
Present
In the last few years, advances in imaging technology and novel treatment modalities have considerably changed the field of functional neurosurgery.
Today, imaging guides clinicians in the planning and execution of stereotactic procedures. In parallel, intraoperative imaging technologies are being developed with the goal of making such procedures more efficient and effective.
Future
From accurate brain imaging technology to improved intraoperative navigation solutions, refined therapeutic paradigms and more, the field of functional neurosurgery will continue to rapidly progress.
In the future, functional neurosurgery procedures will further expand into additional neurological and psychiatric indications and become even more accessible to patients.

Our vision at Brainlab is to offer a platform that analyzes, understands and optimizes patient brain functions. By leveraging the Brainlab data ecosystem and the company’s ever-evolving data enrichment capabilities, we seamlessly incorporate different technologies into scalable, streamlined and optimized functional neurosurgery workflows.
Bring visual clarity and control into surgery
What is deep brain stimulation?
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is an established treatment for people with movement disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor and dystonia whose symptoms cannot be controlled with medications. This approach has also been approved by the FDA to reduce seizures in drug-resistant epilepsy.
DBS involves implanting electrodes within certain areas of the brain to regulate abnormal impulses or affect certain cells and chemicals within the brain. The amount of stimulation in DBS is controlled by a pacemaker-like device placed under the patient’s skin in the upper chest with a wire that travels under the skin and connects this device to the electrodes in the brain.
What is drug-resistant epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a chronic disease of the brain characterized by recurrent seizures. While there are a range of drugs that can effectively treat and manage the disease, not all patients with epilepsy successfully respond to antiseizure medications. These patients are considered to have drug-resistant epilepsy2.
The treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy begins with assessing where the seizures start in a patient’s brain. First, patient’s brain imaging and non-invasive diagnostics such as scalp-EEG are used to identify the area originating the seizures. In case further diagnostic tools are needed, stereoelectroencephalography (sEEG), a procedure in which many electrodes are stereotactically implanted within different regions of the brain, is offered in order to localize the epileptogenic zone. Based on the outcome of the diagnostic steps, patients may undergo other surgical interventions such as partial brain resection, tissue ablation through techniques like laser ablation surgery (LITT) and neuromodulation like DBS.
Access your roadmap to the brain with easy-to-integrate functional neurosurgery software and hardware solutions.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780123970251001184
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy