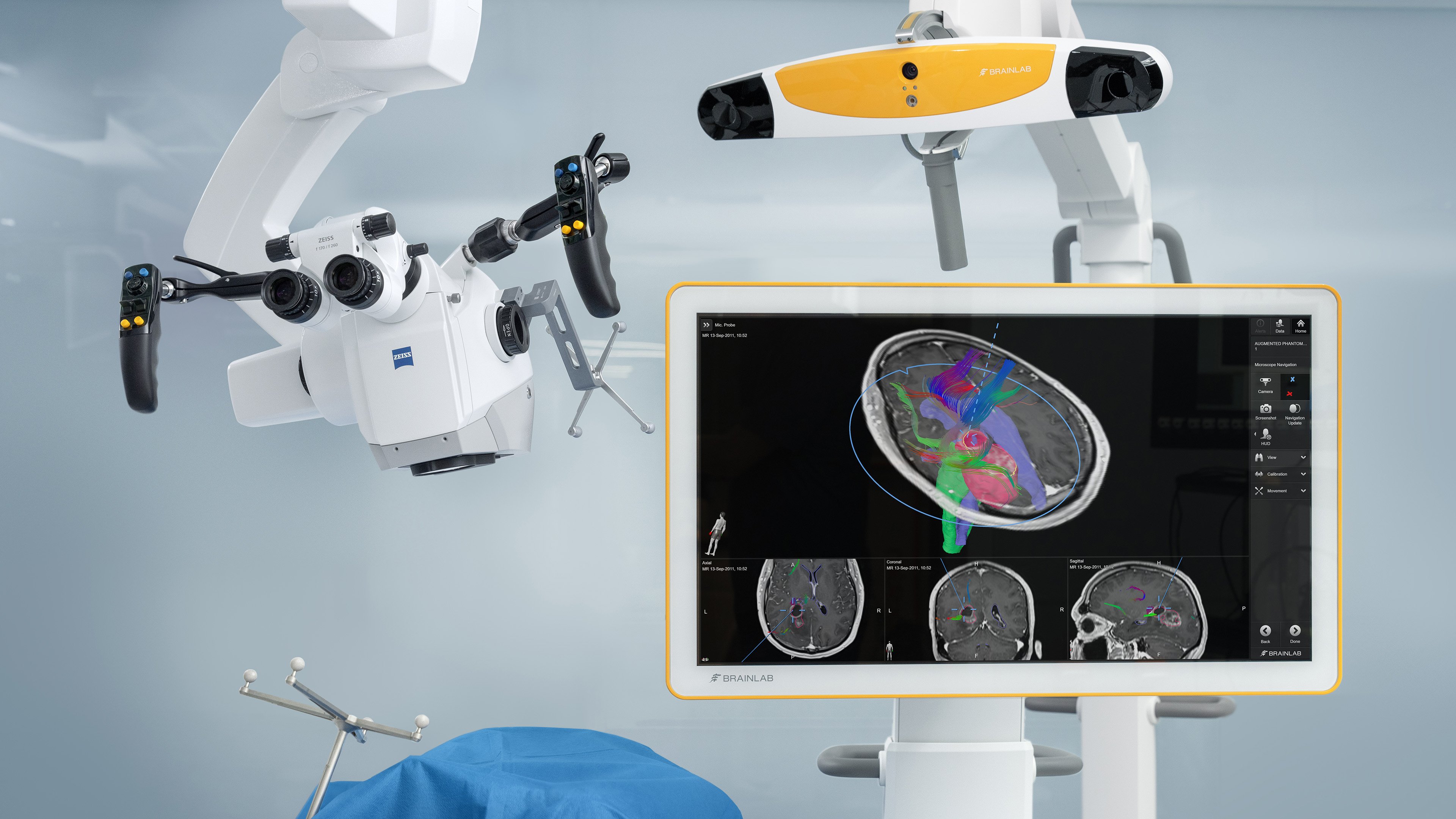
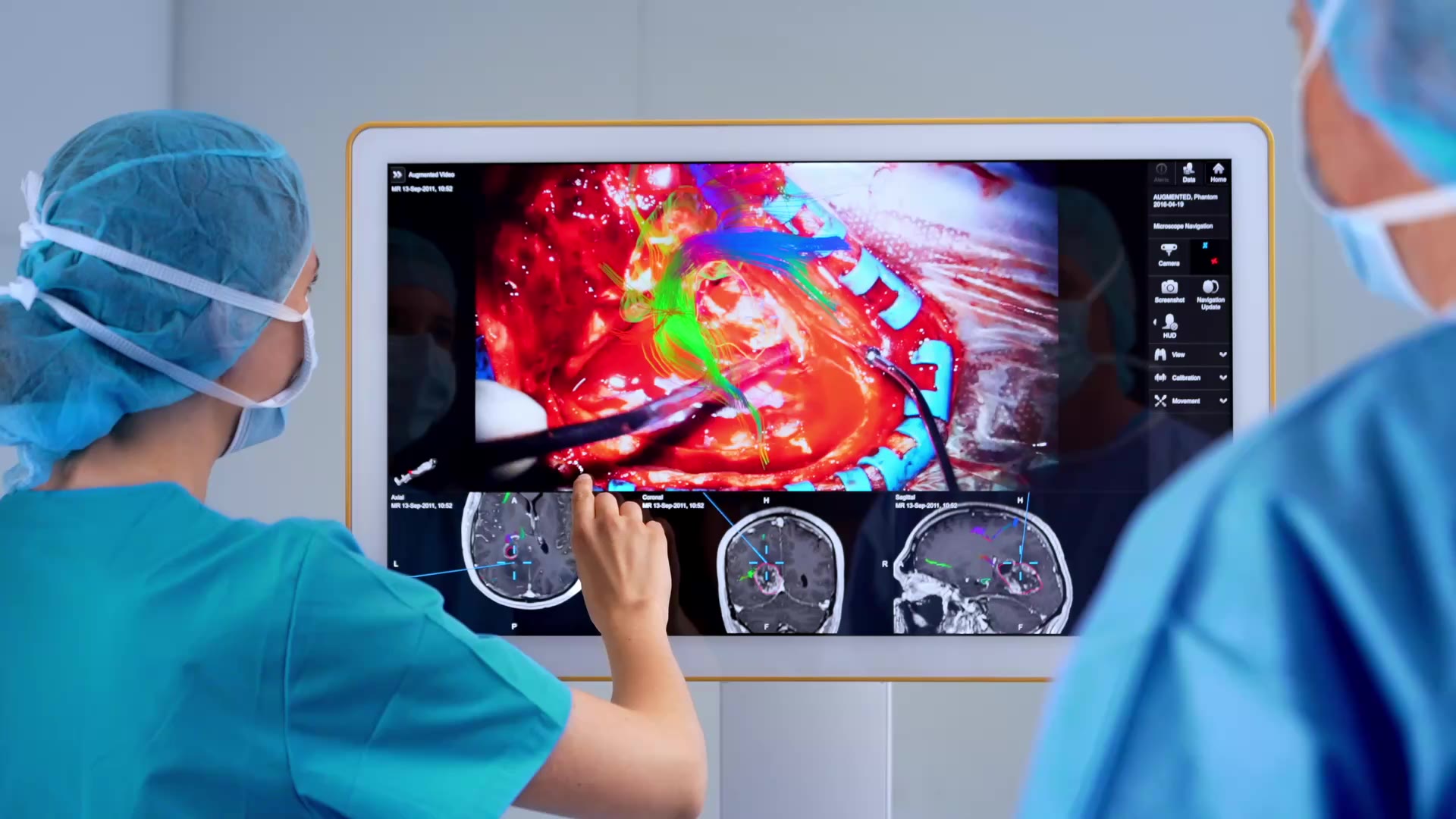
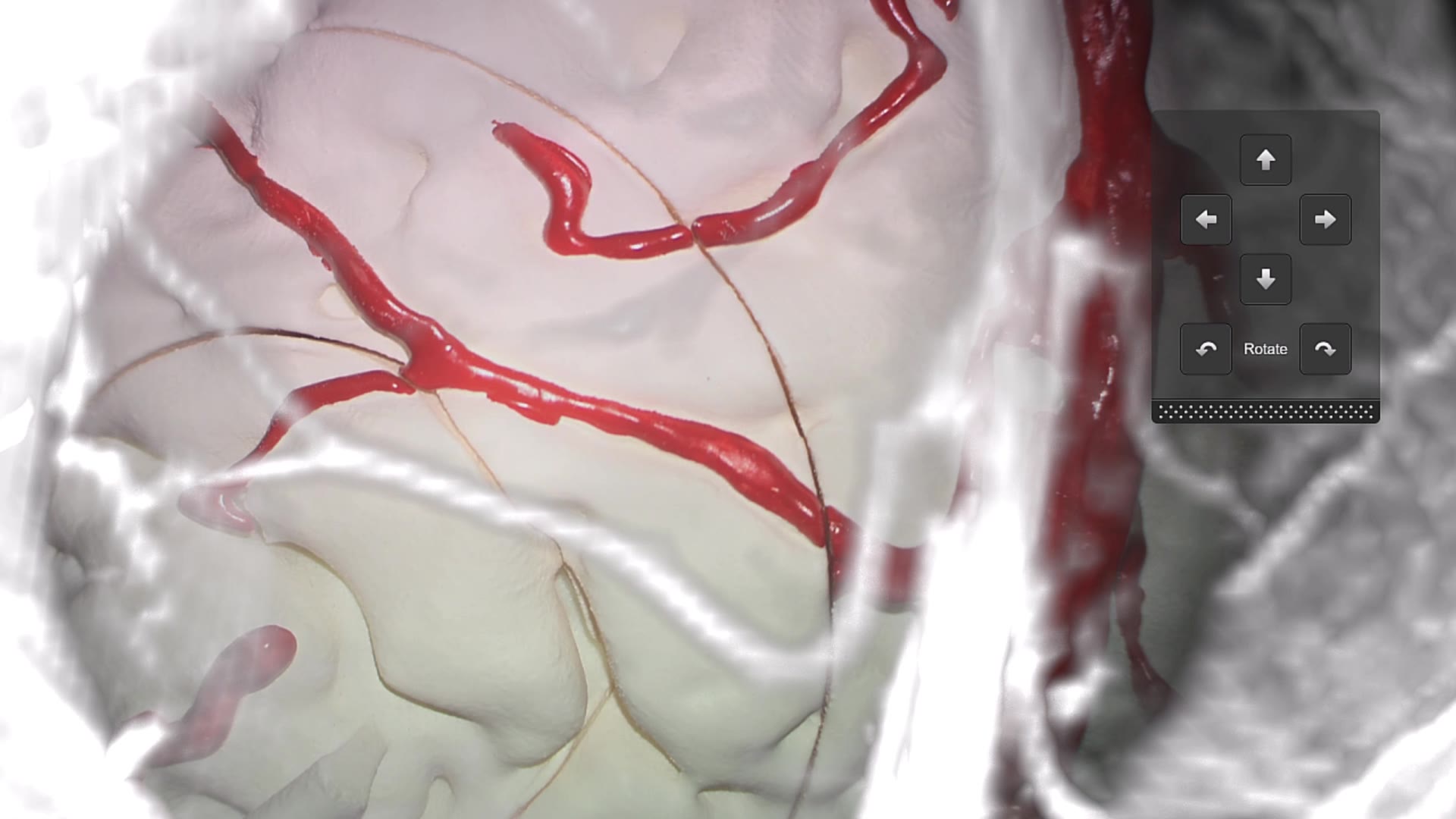
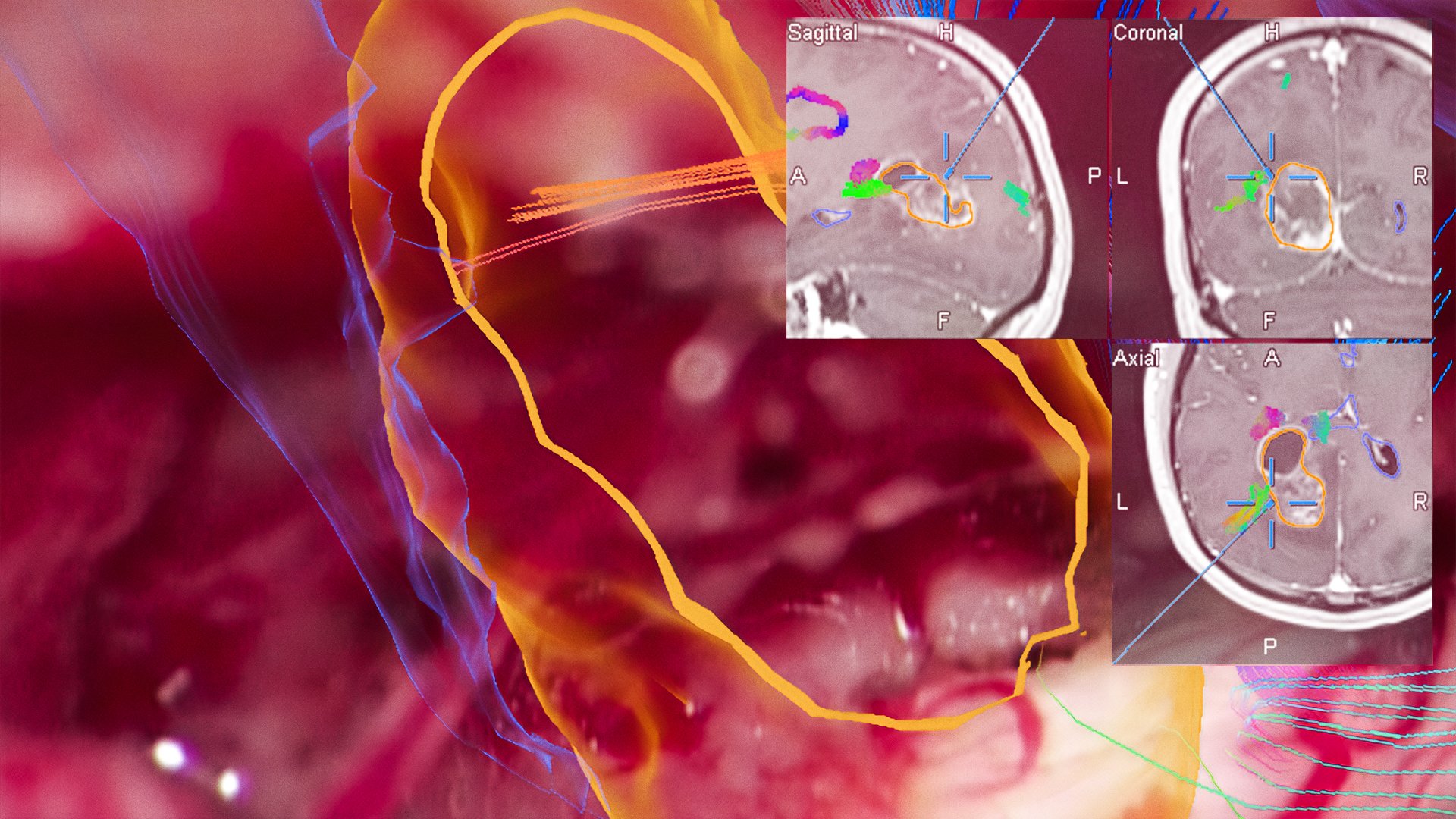
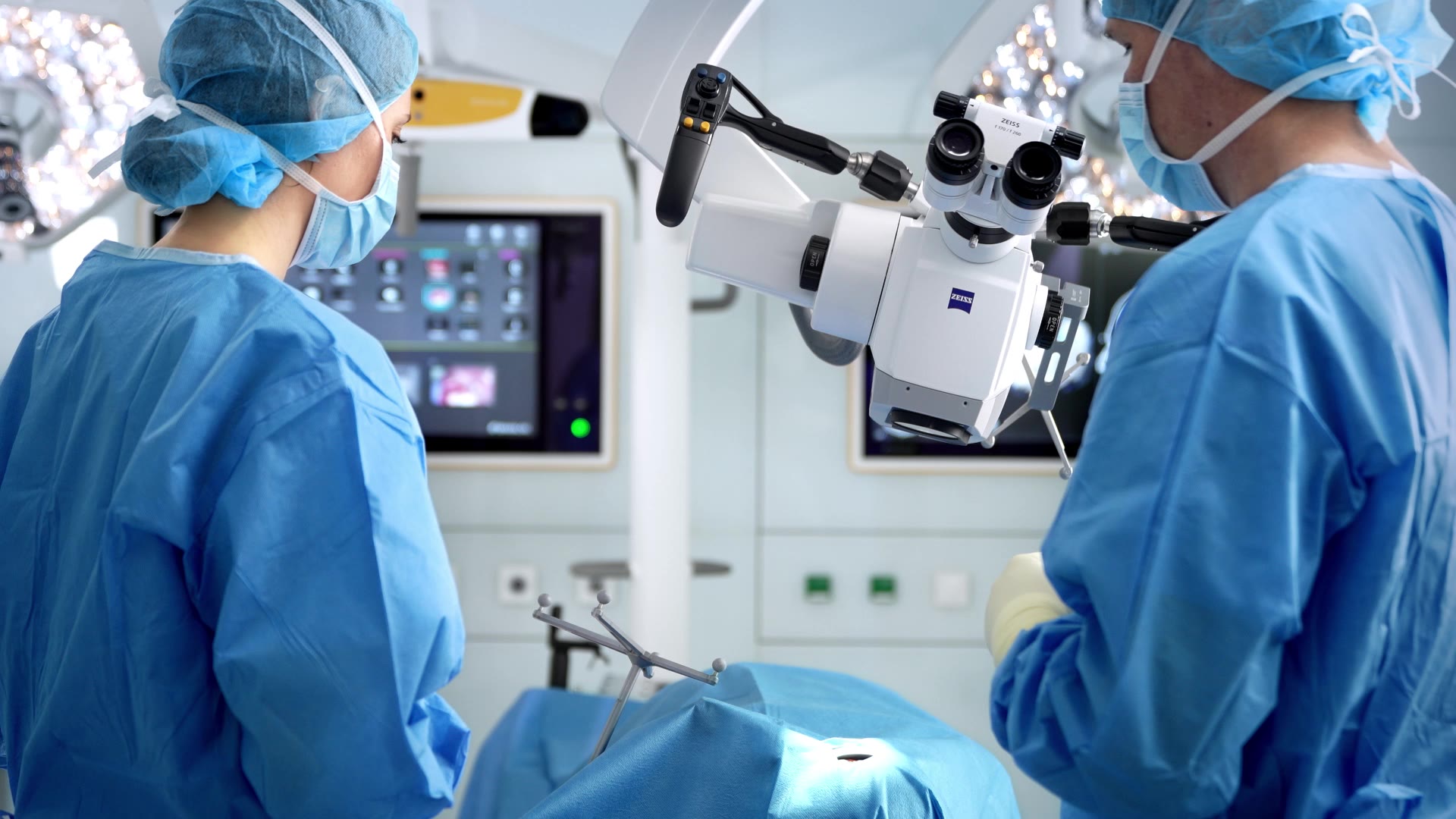
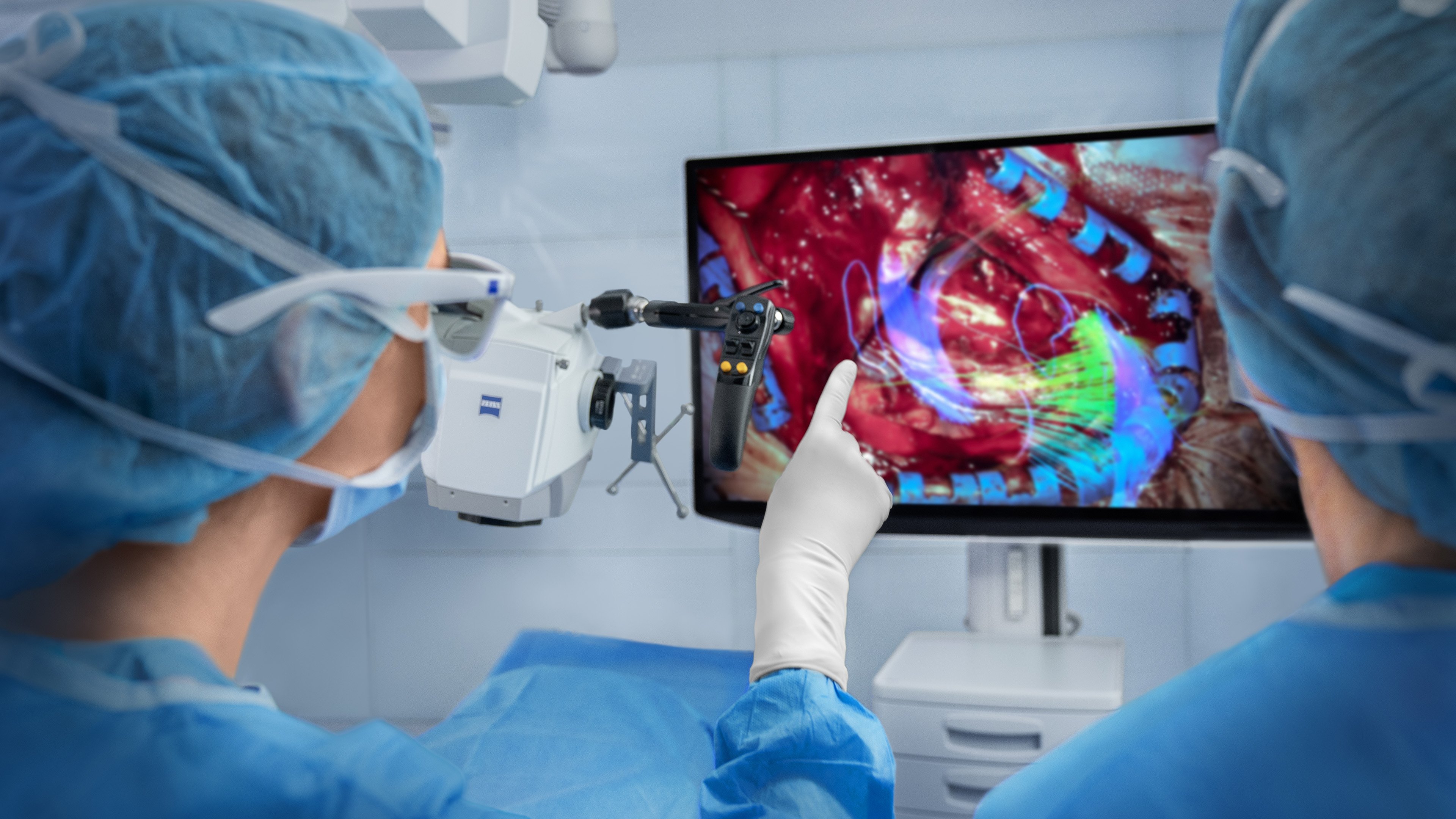
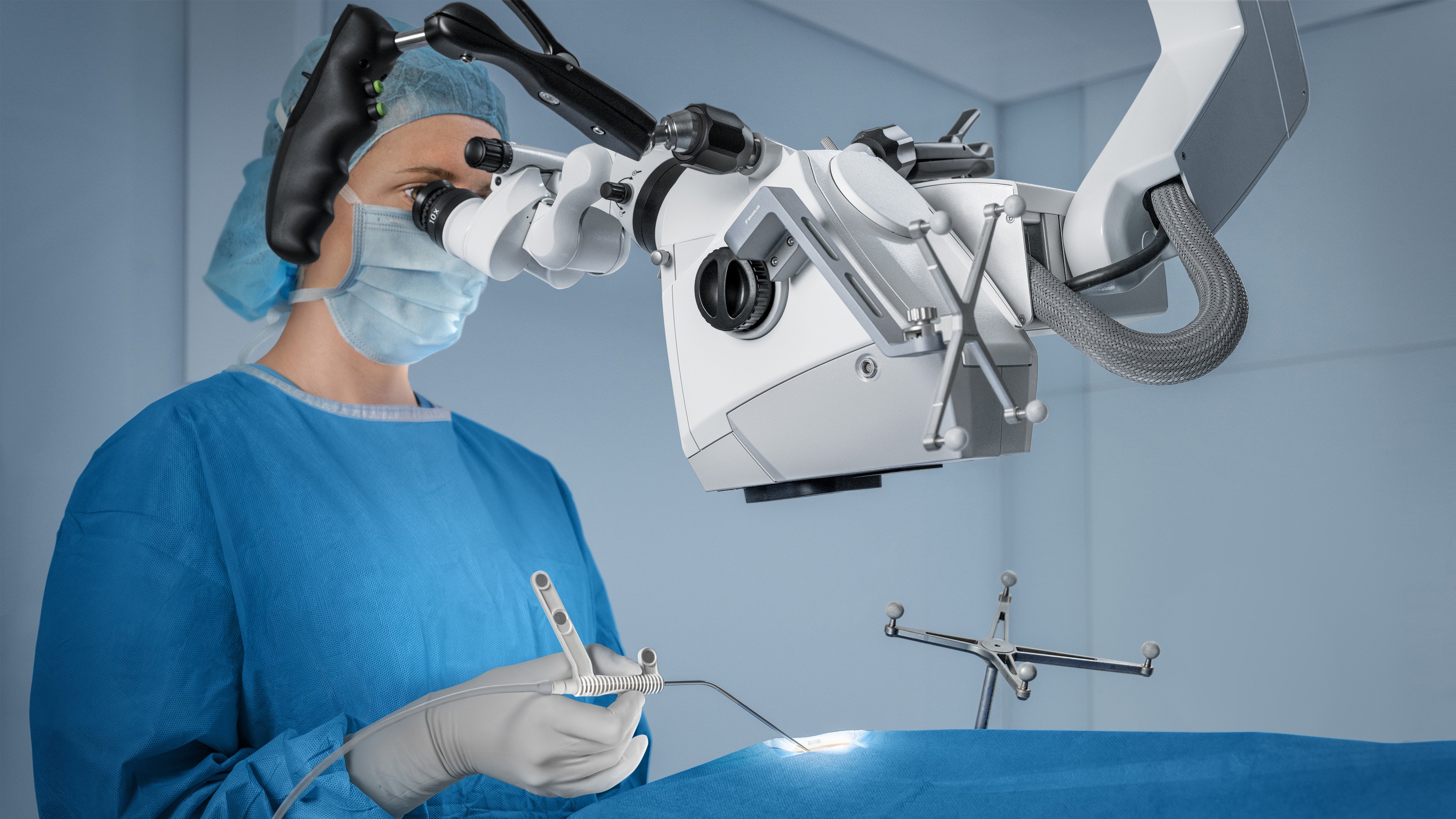
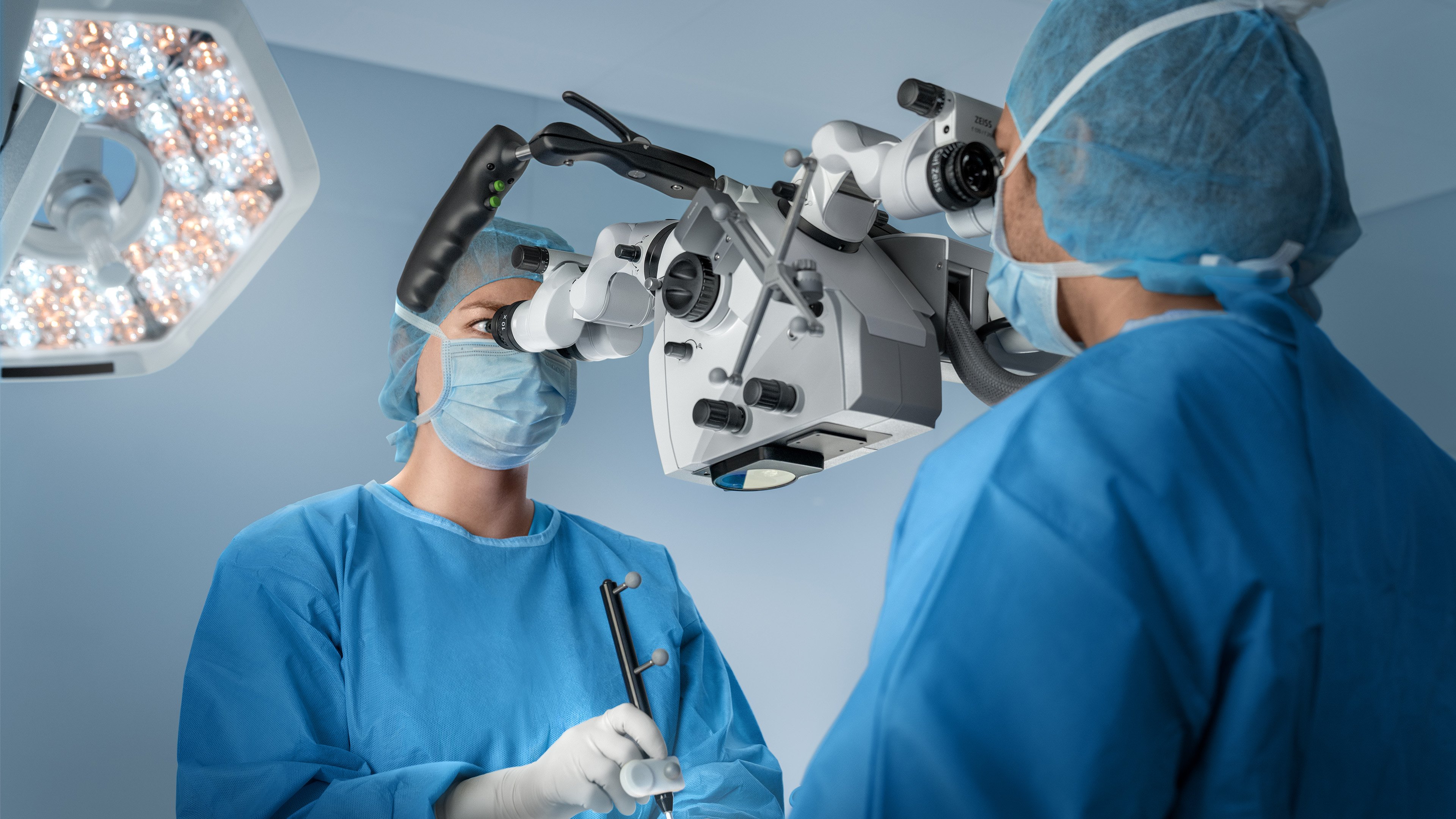
Enhance your view maintain focus
Overlay key structures like tumors, vessels or fiber tracts directly into the microscope view. Surgeons gain real-time spatial context without shifting focus, supporting confident decision-making throughout the procedure.